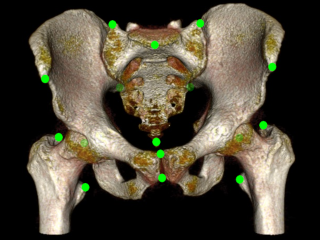
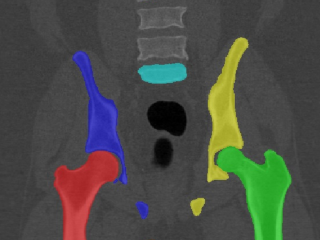
5 bone segmentation masks and 15 annotations of anatomical landmarks for pelvis bones in each of 90 Computed Tomography (CT) cases extracted from the CT Lymph nodes and CT Colonography collections from the The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA).
Keywords: Radiology, Annotated, Pelvis, CT, Computed tomography, Anatomical landmarks, Bone segmentation.
Sample images
Sample images with reduced image quality. Please click to preview.
Dataset information
| Short name | CTPEL |
|---|---|
| Origin | Clinical |
| Cite as |
Bryan Connolly and Chunliang Wang
(2019)
Segmented CT pelvis scans with annotated anatomical landmarks
doi:10.23698/aida/ctpel [BibTeX format] |
| Field | Radiology |
| Organ |
Pelvis |
| Age span | |
| Title | Segmented CT pelvis scans with annotated anatomical landmarks |
| Author |
Bryan Connolly
Chunliang Wang |
| Year | 2019 |
| DOI | doi:10.23698/aida/ctpel |
| Status | Ongoing |
| Version | 1.1 |
| Scans | 90 |
| Annotations | 1800 |
| Size | 28.0GB |
| Resolution | |
| Modality |
CT
|
| Scanner |
|
| Stain | |
| Phase | |
| References | |
| Copyright | Copyright 2019 KTH, Chunliang Wang |
| Access |
Available under the following licenses, described in the License section below.
Controlled access
AIDA license
|
Annotation
Segmentation was done first with an interactive software (Mialab), followed by manual inspection and correction using ITKSNAP. The interactive method is based on fuzzy connectedness followed by level set method. Both the segmentation mask and annotated anatomical landmarks were created by a trained radiologist.
File formats
DICOM. Please see our help pages for some examples of working with DICOM.
Importing binary masks to numpy
The dataset contains a DICOM SEG file, which can be converted to an ITK image file (mha, nifti, etc) by using dcmqi and the command line tool segimage2itkimage, which is straightforward to read into a numpy array.
Landmarks
Landmarks are available in the sr.dcm file and saved using the TID 1500 template.
License
Controlled access
Free for use in research or education.
Help with applying for controlled access.
AIDA BY license
Segmentation masks and anatomical landmark annotations
Copyright 2019 KTH, Chunliang Wang
Permission to use, copy, modify, and/or distribute the data within AIDA (Analytic Imaging Diagnostics Arena https://medtech4health.se/aida) for the purpose of research or education with or without fee is hereby granted, provided that the above copyright notice and this permission notice appear in all copies.
THE DATA IS PROVIDED “AS IS” AND THE AUTHOR DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES WITH REGARD TO THIS DATA INCLUDING ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHOR BE LIABLE FOR ANY SPECIAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES OR ANY DAMAGES WHATSOEVER RESULTING FROM LOSS OF USE, DATA OR PROFITS, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, NEGLIGENCE OR OTHER TORTIOUS ACTION, ARISING OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE USE OR CHARACTERISTICS OF THIS DATA.
Attribution
In addition to the TCIA rules about using the image data, we would really appreciate if you include the following references in publications that make use of the provided segmentation masks or anatomical landmarks:
[1] Bryan Connolly and Chunliang Wang (2019) Segmented CT pelvis scans with annotated anatomical landmarks doi:10.23698/aida/ctpel.